Futures contract specifications play a vital role in the futures market, providing essential contract details that traders need to navigate this complex landscape. Each futures contract includes specifications such as contract sizes, expiration dates, and tick sizes, which help establish a common understanding among buyers and sellers. As an investor considering futures trading, grasping these intricacies is critical, as they directly influence the outcome of your trading activities. Whether you’re engaging in commodity futures or financial instruments like equity indexes, being well-versed in contract specifications can significantly enhance your trading strategy. Understanding these specifications not only shapes your approach but also safeguards you against potential risks in the dynamic world of futures.
In the realm of derivatives, the nuances of futures contracts, often referred to as contract parameters or terms, define the essential framework for market participants. These parameters encompass vital aspects such as the quantity of goods involved, applicable expiration months, and the trading units required for transactions. Investors looking to participate in this sector must familiarize themselves with the details surrounding these contracts, which can vary between commodity markets and financial products. The clarity provided by futures specifications ensures that traders, ranging from large institutions to individual speculators, can operate within a standardized environment that promotes transparency and efficiency. Delving into these intricacies not only unlocks the potential for strategic trading but also enhances understanding of the broader financial landscape.
Understanding Futures Market Dynamics
The futures market operates on the principle of contracts that set forth detailed specifications regarding various commodities, including energy, agricultural products, and financial derivatives. Knowledge of how the futures market operates allows investors, be they small traders or large institutional investors, to navigate its complexities effectively. This understanding encompasses the essential components of trading such as maximum leverage, margin requirements, and market trends which may affect contract pricing.
Moreover, in the futures market, traders must keep an eye on supply-demand dynamics that can lead to fluctuating prices. For instance, if there is a drought affecting corn production, demand may outstrip supply, leading to an increase in prices for corn futures. Thus, analyzing current events and market news becomes crucial for predictive trading and strategic decision making.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential futures contract specifications I should know?
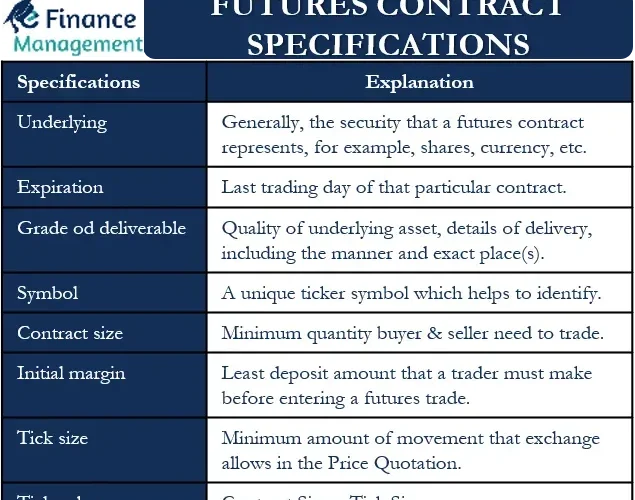
Futures contract specifications include key details like contract size, expiration dates, tick size, and delivery specifications. Understanding these contract specs is crucial for effective futures trading and helps ensure you are aware of your obligations and potential risks.
How do contract sizes differ in various futures markets?
Contract sizes vary across futures markets. For instance, one grain futures contract represents 5,000 bushels, while one crude oil futures contract represents 1,000 barrels. Familiarity with these contract sizes is essential for anyone engaged in commodity futures trading.
What does the term ‘notional value’ mean in relation to futures contracts?
The notional value of a futures contract is calculated by multiplying the contract size by the current market price. This value helps traders assess the scale of their positions in the futures market.
How do expiration dates affect futures trading?
Futures contracts have specific expiration months, which vary by market. For example, corn futures typically expire in March, May, July, September, and December. Being aware of these expiration dates is vital for managing your futures trading strategies.
What is the significance of tick size in futures contracts?
Tick size refers to the minimum price fluctuation for a futures contract. Understanding tick sizes is important for futures traders, as they impact how profits and losses are calculated during trading.
Are futures contracts settled in cash or through physical delivery?
Futures contracts can be either cash settled or physically delivered. Cash-settled contracts settle in cash based on the final price, while physically delivered contracts require the delivery of the commodity. Knowing the delivery specs is crucial for futures traders.
What is the typical trading schedule for futures markets?
Futures markets have varying trading hours; for example, grain futures trade from 9:30 a.m. to 2:20 p.m. ET. Major futures, like E-mini S&P 500 futures, may trade almost around the clock. Familiarizing yourself with these hours is essential for active futures trading.
Why is it important to understand futures contract specifications before trading?
Understanding futures contract specifications is vital because it informs traders of their obligations, risks, and the specific terms of the contracts they engage with. This knowledge enhances decision-making and risk management strategies in the futures market.
How do futures contract specifications influence market liquidity?
Futures contract specifications facilitate market liquidity by standardizing contract terms, making them interchangeable or fungible. This standardization allows a wider range of participants, such as banks and speculators, to engage efficiently in the futures market.
What role do contract details play in risk management for futures trading?
Contract details, including size, expiration, and settlement type, are essential for assessing and managing risks in futures trading. Understanding these specifications allows traders to develop effective strategies and avoid unintentional exposures in their portfolios.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Futures Contract Specifications | Key details outlining quantities, expiration dates, etc. |
| Contract Sizes/Units | Grains: 5,000 bushels; Crude Oil: 1,000 barrels; Gold: 100 troy ounces; Live Cattle: 40,000 pounds. |
| Contract Months | Expiration dates vary by market; e.g., corn futures expire before the 15th of March, May, July, September, and December. |
| Contract Value & Tick Size | Contract value = contract size x current price; minimum price increment is called a tick. |
| Delivery Specifications | Legally binding agreements, obligations to deliver goods unless cash settled. |
| Trading Hours | U.S. trading hours vary; for grains, typically 9:30 a.m. – 2:20 p.m. ET. |
Summary
Futures contract specifications are essential elements guiding market participants in the futures trading landscape. These specifications detail the quantities, expiration dates, and obligations associated with trades, ensuring that both buyers and sellers are fully informed of the implications of their contracts. Understanding these specifications is crucial for anyone engaging in futures contracts, as it aids in assessing the risks and making informed investment decisions. By familiarizing oneself with futures contract specifications, traders can navigate the complexities of the futures market with greater confidence.