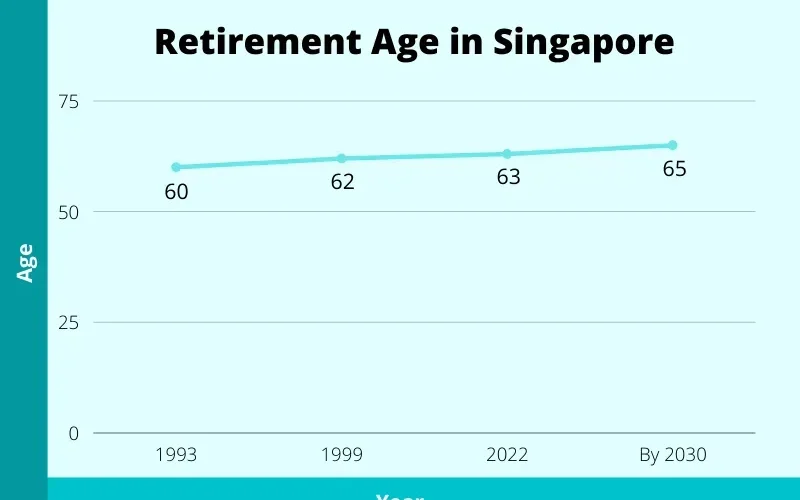Singapore retirement age changes are set to reshape the workforce landscape as the country navigates the challenges posed by an aging population. In 2024, the retirement age remains at 63, but significant adjustments are on the horizon, including a gradual increase to 64 in 2026 and 65 by 2030. This shift not only impacts older employees but also requires employers to adapt to a more experienced workforce. Alongside this, the re-employment age will rise to 69 in 2026, allowing employees to stay engaged longer, which is vital for enhancing CPF retirement savings. As Singapore addresses these demographic changes, the adjustments reflect a commitment to nurturing an inclusive workforce and ensuring economic sustainability.
The upcoming updates to Singapore’s retirement policies signify a pivotal moment in how the nation addresses workforce longevity. With the retirement age adjustments commencing in 2024, the government aims to accommodate the rising number of elder workers while promoting financial security through CPF contributions. These changes, alongside the planned increase in the re-employment age, highlight the importance of skilled older employees who can contribute significantly to various sectors. By fostering a supportive environment for the aging workforce, Singapore not only secures its economic future but also enhances the overall quality of life for its citizens. This proactive approach underscores the need for flexible work arrangements and the potential benefits of extending careers well into the later years.
Understanding Singapore Retirement Age Changes in 2024
As Singapore continues to adapt to the challenges posed by an aging population, the retirement age changes set for 2024 are a crucial part of this strategy. The current retirement age is maintained at 63, but the government plans to incrementally raise it to 64 in 2026 and further to 65 by 2030. This phased approach aims to ensure that older workers can remain a vital part of the workforce, thus contributing to the nation’s economic stability and addressing the growing demand for experienced labor. These changes reflect an understanding of the dynamics of an aging workforce in Singapore, where life expectancy is rising and many individuals are capable of contributing well into their later years.
Moreover, these adjustments are designed to benefit both employers and employees. For businesses, retaining older workers means access to a wealth of experience and institutional knowledge, which can be particularly beneficial in sectors facing skill shortages. For employees, the gradual increase in the retirement age offers an extended opportunity to build their Central Provident Fund (CPF) savings, enhancing financial security as they approach retirement. As Singaporean society evolves, these changes are essential for fostering a sustainable work environment that values the contributions of an aging workforce.
Implications of Retirement Age Increase on Employers
For employers, the increase in the retirement age signifies a need for strategic workforce planning. As the retirement age rises, companies will have the chance to retain seasoned employees longer, which can mitigate the impact of skill shortages in critical areas such as healthcare and technology. This retention not only preserves the knowledge and skills that older workers bring but also helps organizations maintain continuity and stability during transitions. Employers must adapt their policies to support an aging workforce, including offering flexible work arrangements that accommodate the needs of older employees.
Additionally, the rising re-employment age, from 68 to 69 by 2026, will encourage organizations to rethink their workplace culture. Implementing initiatives like phased retirement, part-time positions, and hybrid work models can significantly enhance job satisfaction among older workers. This adaptability not only benefits the employees but also positions companies as attractive employers in a competitive market. The government’s support through grants and incentives can further assist businesses in creating age-friendly workplaces, making the transition smoother for all parties involved.
Benefits of Retirement Age Changes for Employees
The recent changes to Singapore’s retirement age present numerous benefits for employees, particularly those nearing the end of their careers. By allowing individuals to work beyond the traditional retirement age, employees have increased opportunities to enhance their financial security. This is especially crucial in a high-cost living environment like Singapore, where savings accumulated in the Central Provident Fund (CPF) can significantly impact one’s quality of life during retirement. Continued employment means not only larger CPF contributions but also the potential for higher retirement payouts.
Furthermore, the flexibility introduced by these changes allows older employees to tailor their work-life balance more effectively. Many workers may wish to continue contributing to the workforce for personal fulfillment or financial necessity, and the option to negotiate part-time or flexible roles can help accommodate these needs. This shift not only fosters a sense of purpose among older workers but also ensures that their skills and experiences continue to benefit the workplace.
Challenges Faced by Older Workers in the Workforce
While the increase in retirement and re-employment ages provides opportunities, it also presents challenges for older workers. Not every senior employee may have the physical or mental capacity to continue working past their 60s. It is essential for policymakers and employers to recognize these limitations and create supportive environments that focus on health and well-being. Implementing wellness programs and providing access to healthcare resources can help mitigate these challenges, ensuring that older employees can work effectively and remain productive.
Additionally, older workers may face age discrimination in the workplace, making it difficult for them to secure employment or advancements. To combat this, organizations must cultivate an inclusive culture that values diversity and the unique contributions of older employees. Training programs aimed at fostering intergenerational collaboration can help bridge the gap between younger and older workers, ultimately enriching the workplace. By addressing these challenges head-on, Singapore can create a more equitable environment for all employees, regardless of age.
The Role of CPF in Retirement Planning
The Central Provident Fund (CPF) remains a cornerstone of retirement planning for Singaporeans. Despite changes in the retirement and re-employment ages, the CPF withdrawal ages will not be affected, allowing individuals to access their savings at 55, subject to conditions. Furthermore, the introduction of the Enhanced Retirement Sum (ERS) provides an opportunity for individuals to contribute more to their CPF, which can lead to increased payouts during retirement. This strategic planning is vital for those who wish to ensure a comfortable retirement, especially amid rising living costs.
Additionally, the CPF LIFE scheme continues to be a reliable source of income for retirees, providing financial stability during their later years. As individuals work longer, they can take advantage of CPF’s voluntary topping-up schemes, which encourage enhanced contributions towards their retirement savings. This dual approach of working longer and maximizing CPF contributions can significantly bolster retirement finances, enabling Singaporeans to enjoy a financially secure retirement.
Strategies for Effective Retirement Planning Post-Changes
In light of the upcoming changes in retirement and re-employment ages, it is essential for individuals to reassess their retirement planning strategies. Assessing one’s financial goals is the first step; utilizing CPF calculators or consulting financial advisors can provide clarity on how the changes may affect personal savings. Planning ahead is crucial, especially as the increase in retirement age may necessitate adjustments in how individuals save and invest for their future.
Moreover, maximizing CPF contributions is a key strategy for those who plan to work beyond the current retirement age. Engaging in the Retirement Sum Topping-Up Scheme can further enhance one’s retirement savings, providing a more substantial financial cushion. Exploring flexible work options with employers can also facilitate a smoother transition into retirement, allowing individuals to maintain engagement with the workforce while managing their health and personal circumstances. Ultimately, proactive planning is essential to navigate these changes effectively.
Navigating Flexible Work Options for Older Employees
As the retirement age increases, the introduction of flexible work options becomes increasingly important for older employees. Many individuals may wish to continue working but may prefer part-time roles or flexible schedules that better suit their lifestyles. Employers are encouraged to adopt policies that facilitate these arrangements, such as job-sharing or telecommuting, which can help retain older workers while ensuring they do not feel overwhelmed by traditional full-time demands.
Implementing flexible work arrangements not only benefits older employees but also enhances overall workplace morale and productivity. Organizations that embrace these changes can tap into the wealth of experience that older workers bring, while also demonstrating a commitment to employee well-being. This mutual respect between employers and employees fosters a more inclusive workplace culture, supporting a diverse talent pool that includes individuals of all ages.
The Future of Singapore’s Workforce: Embracing Aging
The future of Singapore’s workforce will increasingly involve embracing the aging population as a valuable asset. With the retirement age set to rise, it is crucial for society to shift perspectives on aging and recognize the contributions that older employees can make. By fostering an environment that values experience and knowledge, Singapore can enhance its productivity and innovation across various sectors. This cultural shift is necessary to combat stereotypes and promote the benefits of an age-diverse workforce.
Moreover, as companies adapt to these changes, they will need to invest in training and development programs tailored for older workers. Upskilling initiatives can help seniors remain competitive and proficient with new technologies and methodologies. By integrating older workers into the fabric of the workforce, Singapore can maintain a robust economy while addressing the challenges posed by an aging demographic. This approach not only benefits individuals but also contributes to the broader goal of economic sustainability and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Singapore retirement age changes for 2024?
In 2024, the retirement age in Singapore remains at 63 years. However, it is set to increase to 64 years in 2026 and will reach 65 years by 2030. These changes reflect Singapore’s efforts to adapt to an aging workforce and ensure that older workers can continue to contribute to the economy.
How will the retirement age increase in Singapore affect CPF retirement savings?
The upcoming changes to the retirement age in Singapore do not directly affect the CPF withdrawal ages, which remain at 55 for accessing savings. However, the adjustments encourage individuals to enhance their CPF retirement savings through schemes like the Retirement Sum Topping-Up Scheme, allowing for greater financial security as they work longer.
What is the re-employment age change in Singapore for 2026?
Starting in 2026, the re-employment age in Singapore will increase from 68 to 69 years, with a further increase to 70 years by 2030. This change aims to allow older employees to continue contributing to the workforce, thereby addressing the challenges posed by an aging population.
Why are Singapore retirement age changes important for the aging workforce?
The retirement age changes in Singapore are crucial for managing an aging workforce. By raising the retirement and re-employment ages, the government is ensuring that older workers can remain in the labor market longer, which helps maintain productivity and supports economic stability amidst demographic shifts.
What benefits do the Singapore retirement age changes bring to employees?
Employees benefit from the changes to Singapore’s retirement age as they can continue working beyond the traditional retirement age, allowing them to accumulate more savings and enjoy greater financial security. Additionally, the changes promote flexible work arrangements, enabling a better work-life balance.
How can employers adapt to the retirement age changes in Singapore?
Employers in Singapore can adapt to the retirement age changes by implementing flexible work arrangements such as part-time roles, job-sharing, and remote work options. This approach not only accommodates older workers but also helps businesses retain valuable talent, especially in sectors facing skill shortages.
What are the implications of the Singapore retirement age changes on workforce planning?
The changes to the retirement age in Singapore necessitate a reassessment of workforce planning strategies. Employers should consider retaining older employees, while employees need to evaluate their financial and career goals in light of the extended working ages, ensuring they are prepared for retirement.
How do the Singapore retirement age changes affect workers’ health and wellness?
As Singapore raises its retirement age, it becomes increasingly important for employers to support the health and wellness of older workers. Providing wellness programs and ergonomic workspaces can help ensure that senior employees remain healthy and productive as they continue their careers.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Retirement Age (2024) | 63 years |
| New Retirement Age (2026) | 64 years |
| Re-employment Age | Currently 68; increasing to 69 by 2026 and 70 by 2030 |
| Reason for Changes | Increasing life expectancy and the need for a larger, more experienced workforce |
| Flexibility for Employers and Employees | Flexible work arrangements and part-time opportunities available for older workers |
| Impacts on CPF | Retirement age changes do not affect CPF withdrawal ages, but there are opportunities to increase retirement savings |
Summary
Singapore retirement age changes are set to reshape the future of work for older employees. As the retirement age remains at 63 in 2024, it will gradually rise to 64 in 2026 and 65 by 2030, while the re-employment age will also increase. This strategic adjustment not only addresses the challenges posed by an aging population but also ensures that older workers can continue contributing to the economy. By providing flexible work arrangements and encouraging financial planning through CPF enhancements, these changes create a more sustainable and inclusive workforce for Singapore.